| Search for content and authors |
Nano-inks for printing electric circuits for microelectronics technology |
| Andrzej E. Kinart , Andrzej J. Mościcki |
|
Amepox Microelectronics, Ltd. (AMEPOX-MC), Jaracza 6, Łódź 90-268, Poland |
| Abstract | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The ink-jet is non-contact technique for production very complicate electronic patterns like conducting points, lines and even 3D structures for electronic applications. There are several important components of the ink-jet printing technology for electronic: the printing system, the conductive ink material and substrates. The greatest challenge is the ink formulation, because these inks have to meet strict physicochemical properties: viscosity, surface tension, adhesion to a substrate, sintering temperature, etc. The most important is low viscosity and very homogeneous structure like molecular fluid with conductive nanosized particles. This type of fluids must be stable for a long time to avoid sedimentation during printing process and to achieve optimal performance and reliability of the printing system and obtain the best printed pattern. Amepox Microelectronics developed two inks: high sintering temperature (230oC) with particles size 3-8 nm (Fig. 1a) - trade name AX JP-6n and low sintering temperature (150oC with particles size 50-60 nm (Fig. 1b) - trade name AX JP-60n. 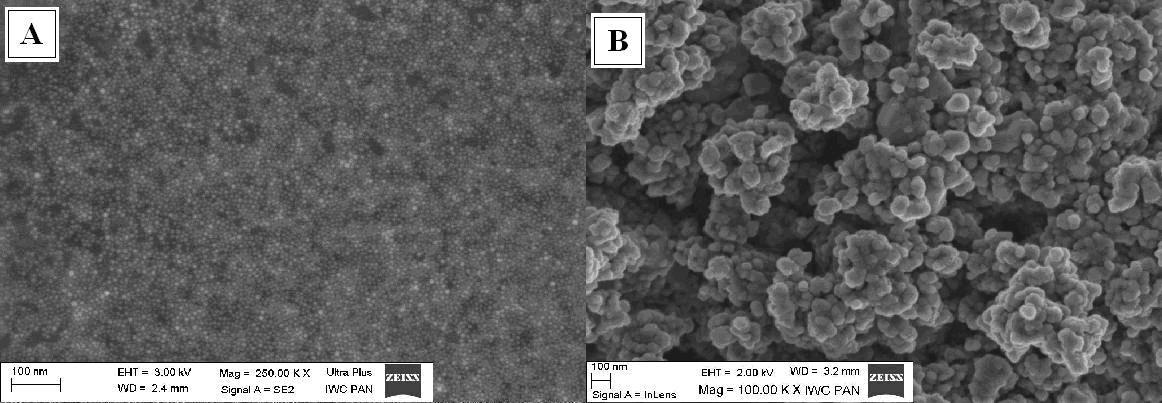
Fig .1 A – Nanosilver 3-8 nm, B – Nanosilver 50-60nm The Inks have very high and stable electrical conductivity near value of pure silver. Inks natures (connected with molecular fluid properties) are perfectly homogeneous – fully uniform silver concentration in whole ink volume. This is also reason for very good repeatability of resistance and dispensed shapes: dots, lines, etc. The main technical parameters of the inks you can see in the Table 1. Table1. Technical parameters of inks.
(*) - Brookfield LVDVII + CP; 100 rpm; 20°C.
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Legal notice |
|
| Related papers |
Presentation: Oral at Nano PL 2014, Symposium A, by Andrzej E. KinartSee On-line Journal of Nano PL 2014 Submitted: 2014-10-06 12:18 Revised: 2014-10-06 12:18 |