Long-chain arylpiperazines (LCAPs) represent one of the most important classes of
5-HT1A receptor ligands [e.g. buspirone, tandospirone, NAN-190, flesinoxan, WAY 100135]. Most of the ligands with high affinity for the 5-HT1A receptor exhibit a high level of undesired affinity for α1-adrenergic receptor [1].
Structural modification within LCAPs occurs mainly at the two opposite ends of the molecule and can significantly influence both their affinity and functional profile at 5-HT1A receptors [2-4].
The aim of the work, which is a continuation of our previous study, was to synthesize new analogues of buspirone (key structure), with higher affinity and selectivity to 5-HT1A receptors [5-7]. A series of new 4-aryl-perhydro-pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine derivatives with an arylpiperazine moiety have been obtained. Multi-stage preparations were used to obtain pure diasteromer (1R,4aS) 4-phenyl-perhydro-pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-2,4-dione, being the starting compound for further modification. N-alkilation of the imide group in (1R,4aS) 4-phenyl-perhydro-pyrrolo[1,2-a]pyrazine-2,4-dione, with 1,4-dibromobutane was used to yield monobromobutyl derivative.
The final new ligands were obtained by the condensation of appropriate arylpiperazine with the above described monobutyl derivative.
The structure of new compounds was confirmed by 1H and 13C NMR spectral data and X-ray diffraction data as well as by C, H, N analysis.
The final compounds will be submitted to screening test to elucidate the affinity for 5-HT1A receptors.
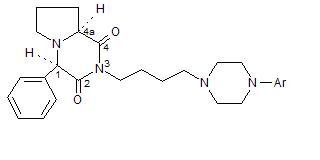 |
Ar = phenyl, 2-pyridyl, 2-pyrimidinyl,
2-fluorophenyl, 2-tolyl,
2-chlorophenyl, 2-methoxyphenyl,
3-trifluormethylphenyl |
[1] Trumpp-Kallmeyer S. et al.; J. Med. Chem. 35, 3448 (1992)
[2] Perrone R. et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. 8, 873 (2000)
[3] Caliendo G. et al.; Bioorg. Med. Chem. 8, 533 (2000)
[4] Lopez - Rodriguez M. L.; J. Med. Chem. 42, 36 (1999)
[5] Herold F. et al.; Farmaco 57, 959 (2002)
[6] Herold F. et al.; Pharmazie 59, 99 (2004)
[7] Herold F. et al.; Eur. J. Med. Chem. in press 2006 |