| Search for content and authors |
Graphene nanocomposite for the reversible hydrogen storage |
| Piotr Kula , Robert Pietrasik , Konrad Dybowski , Radomir Atraszkiewicz , Witold Szymański , Łukasz Kołodziejczyk |
|
Lodz University of Technology, Institute of Materials Science and Engineering, Stefanowskiego 1/15, Lodz 90-924, Poland |
| Abstract |
|
Acronym: GraphRoll Title: Graphene nanocomposite for the reversible hydrogen storage use Project no.: GRAF-TECH/NCBR/07/24/2013 Duration: January 1st, 2013 – December 31st, 2015 Consortium: 1. Lodz University of Technology, Łódź, Poland 2. SECO/WARWICK S.A., Świebodzin, Poland Objectives and methods: The main aim of the project is to work out the technology for producing the functional nanocomposite material „GraphRoll” on the basis of polycrystalline graphene for reversible storage of hydrogen. The area for a potential application of the new nanomaterial in the nearest time horizon will be industrial technological facilities for heat and thermo-chemical treatment where hydrogen is a process medium or is used in high pressure gas quenching. Pumpless compressors based on „GraphRoll” will be provided for hydrogen recycling in the processes of High Pressure Gas Quenching (HPGQ) as well as for hydrogen separation from exhaust mixtures of gases during operations of thermochemical treatment (low pressure carburizing - FineCarb and PreNitLPC). Moreover, upon further improvement of the technology, it is expected that these new materials, when reaching the critical threshold of 6.5% wt. hydrogen absorption on an industrial scale, will be used for the storage of hydrogen in the vehicles of the future. 
The nanostructure of that nanocomposite is based on the original method of polycrystalline graphene synthesis from the liquid phase. In the next stages the graphene is decorated by PVD spark and/or laser sputtering, then separated from the surface and finally rolled helically around the core fiber to reach 3D helical nanostructure with strongly developed area of active graphene with oligomeric pillars in between (Figure 1). Results: The obtained results confirmed that the reported method of graphene manufacturing from the liquid phase could be successfully used (Figure 2).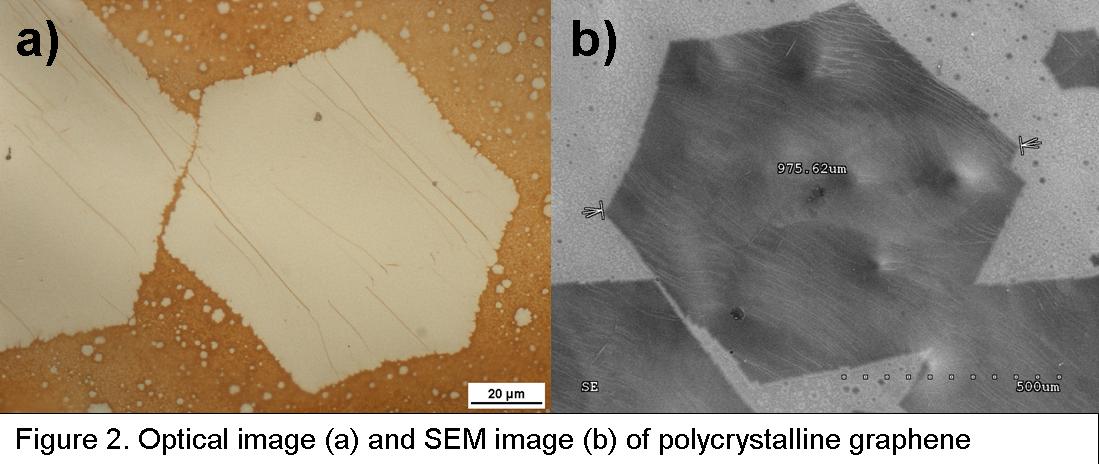 The intermediate structures could be also synthesized and it is possible to study the mechanisms of graphene nucleation and growth. Moreover this technique allows to produce large graphene panels, so they will provide a base for the production of nanocomposites targeted at hydrogen storage applications.
The intermediate structures could be also synthesized and it is possible to study the mechanisms of graphene nucleation and growth. Moreover this technique allows to produce large graphene panels, so they will provide a base for the production of nanocomposites targeted at hydrogen storage applications. |
| Legal notice |
|
| Related papers |
Presentation: Polish Research Projects at Nano and Advanced Materials Workshop and Fair, by Piotr KulaSee On-line Journal of Nano and Advanced Materials Workshop and Fair Submitted: 2013-07-04 14:26 Revised: 2013-07-30 00:02 |