| Search for content and authors |
The biological activity of quinoline derivatives |
| Ewelina Spaczyńska 1, Dominik Tabak 1, Agnieszka Szurko 2, Robert Musioł 1 |
|
1. University of Silesia, Institute of Chemistry (UŚ), Szkolna 9, Katowice 40-006, Poland |
| Abstract |
Compounds containing quinoline moiety are well known due to their broad biological activities. A number of them have been widely investigated and clinically used as antifungal or antibacterial agents [1, 2]. Quinoline derivatives have gained strong attention recently due to their activity as perspective HIV integrase inhibitors [3]. Recently, some quinoline-based compounds have been synthesized and reported as potent antitumor agents by our research team [4]. Anti-proliferative activity of the synthesized compounds was tested by the MTS assay against the human colon adenocarcinoma cell lines with normal expression of p53 protein (Hct116 p53+/+) and mutants with disabled TP53 gene (Hct116 p53-/-). The compounds were also tested for their cytotoxicity against mouse melanoma cell line B16-F10 and nontumor cell line NHDF. Anti-proliferative activity of quinoline derivatives was determined. Compound (Figure 1) demonstrated the highest anti-proliferative activity (IC50=1,40µM). The most active compound makes it promising for further development. 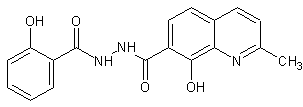
Figure 1. Chemical structure 8-hydroxy-N'-(2-hydroxybenzoyl)-2-methylquinoline-7-carbohydrazide. References: [1] Musiol R., et al., Bioorganic Medicinal Chemistry, 2006, 14, 3592-3598. [2] Palit P., et al., European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry, 2009, 44, 845-853. [3] Zouhiri F., et al., Tetrahedron Letters, 2005, 46, 2201-2205. [4] Musiol R., et al.,Bioorganic Medicinal Chemistry, 2007, 15, 1280-1288.
|
| Legal notice |
|
| Related papers |
Presentation: Poster at IX Multidyscyplinarna Konferencja Nauki o Leku, by Ewelina SpaczyńskaSee On-line Journal of IX Multidyscyplinarna Konferencja Nauki o Leku Submitted: 2014-03-26 17:24 Revised: 2014-05-02 19:12 |