| Search for content and authors |
Single Domain Maghemite Nanoparticles and Nanocomposites using Chitosan for Dye Removal from Industrial Waste Water |
| Saravanan Annamalai , Suraiya Begum , Radha Perumal Ramasamy |
|
Anna University, Department of Applied Science and Technology, ACT campus (ACT), Chennai 600 025, India |
| Abstract |
Chitosan is a natural, biodegradable and biocompatible polymer which is having an excellent film forming ability [1]. Maghemite (γ-Fe2O3) is one of the oxides of the iron and it is used for the preparation of polymer magnetic nanocomposites because of its unique superparamagnetic behavior, biocompatibility, non-toxicity and low cost of production. Chitosan-maghemite nanocomposites have great potential applications in various biomedical fields and in environmental engineering like for heavy metal ion removal and dye detection. [2,3] In this work, chitosan-maghemite nanocomposites were prepared by the following steps. In the first step, single domain maghemite nanoparticles were prepared by a standard co-precipitation method [4]. The size of the nanoparticles was found to be ~ 3 nm using scherrer formula. In the second step, the as obtained mahemite nanoparticles were dispersed in to the 1(w/v) chitosan along with the 1.5% acetic acid solution by ultrasonic irradiation for 10 min at various concentrations of maghemite. After sonication, the composite solution was poured into a glass plate and dried at room temperature for 3 days. As obtained films were found to be flexible. The colour of the films turned from yellow to dark brown as the concentration of the maghemite nanoparticles increased from 0 to 50%. XRD, FE-SEM, VSM and dielectric measurements were taken for the obtained maghemite nanoparticles. The particles were found to be spherical, superparamagnetic and having high dielectric constant. The Chitosan – Maghemite nanocomposite showed that the particles are dispersed throughout the film [Fig. 1]. The structure of the chitosan-maghemite nanocomposites were characterized by XRD. Both high resolution scanning electron microscopy (HR-SEM) and Atomic Force microscope (AFM) were used to characterize the dispersion of γ-Fe2O3 NPs on the chitosan matrix and the surface morphology of the nanocomposites. The effect of the γ-Fe2O3 NPs on the chitosan also was studied by using the thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The various dielectric charecteristics like dielectric constant, loss, electric modulus and conductivity were studied as a function of frequency (0.01Hz to 1MHz) and temperature (300C to 1500C). The morphology and the dielectric charecetristics were found to be dependent upon the concentration of the nanoparticles while the magnetic property was found to be nearly the same for low (5%) and high (50%) concentration of maghemite nanoparticles. The efficiency of the nanocomposites in removing methyl orange dye from water will also be discussed.  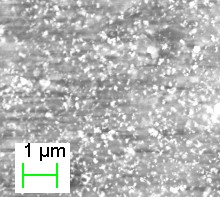 Figure 1 Optical and SEM images of the Chitosan - maghemite nanocomposites References: 1. Denkbas E. B.et al, React. Funct.Polym., 50,225 (2002) 2. Chang YC et al., J. Colloid Interface Sci. 283, 446 (2005) 3. R. Jiang et al., J Appl Polym Sci 125, 540 (2012) 4. Laurent S et al.,Chem. Rev. 108, 206 (2008) |
| Legal notice |
|
| Related papers |
Presentation: Poster at 17th International Conference on Crystal Growth and Epitaxy - ICCGE-17, General Session 8, by Saravanan AnnamalaiSee On-line Journal of 17th International Conference on Crystal Growth and Epitaxy - ICCGE-17 Submitted: 2013-04-14 11:00 Revised: 2013-07-25 11:55 |