The β2 adrenergic receptor (β2-AR) belongs to the large and diverse family A of G-protein-coupled receptors. Both, the bovine rhodopsin (1F88) and the human β2-AR (2RH1) were crystallized in their inactive states. The human β2-AR was crystallized with bound inverse agonist – carazolol. The molecular model of the β2-AR has already been proposed by Furse and Lybrand. This model has been initially constructed by means of comparative modeling techniques based on the rhodopsin template and was further optimized in order to properly reflect experimental results for β adrenergic receptors.
Our study concentrates on comparison of the results of docking studies to the three models of β2-AR:
1) the complete model of β2-AR (conformation of N-, C-termini and loop connecting TM5 and TM6 were predicted using de novo methods)
2) the model presenting the active state of β2-AR (initial receptor structure of complete model of β2-AR was optimized to preserve receptor-ligand interactions for set of typical agonists applying restrained simulated annealing procedure).
3) the hybrid model of β2-AR (model based mainly on the Furse and Lybrant model but some of its features were common to the crystal structure of β2-AR).
In particular, docking studies were applied to the set of fenoterol derivatives (n = 32), in case of which the enantioselectivity plays a crucial role. The ligands were docked into one binding site using several docking procedures. The Molegro Virtual Docker (MVD) software was employed for this purpose. Agonist molecules occupy the same binding region, located between TM3, TM4, TM5, TM 6 and TM7. The following residues identified by us during docking procedure were experimentally indicated in functional and biophysical studies as being very important for formation of the hydrogen bonds: Ser204, Ser207, Asp113, Asn293, Tyr308 (Figure 1). Docking results were analyzed in terms of scoring functions (MolDock Score, Rerank Score, Similarity Score, Docking Score). Correlations between the function score values and the compound binding affinities (the latter expressed as Ki values) were examined. According to our study, docking in Molegro Virtual Docker offers a good prediction of the binding energies (expressed as the scoring function values). The correlation between the MolDock Score and the experimentally determined pKi is depicted by the determination coefficients R2=0.4767 and R2=0.427 for the hybrid and the crystal model, respectively. In addition, molecular dynamics simulations of obtained complexes were carried out. Systems under consideration consisted of receptors with bound ligands embedded into POPC membrane model in water environment. Trajectories obtained from the MD simulations gave us better insight into receptor-ligand interactions and system evolution. All calculations were performed applying GROMACS 3.3 software package.
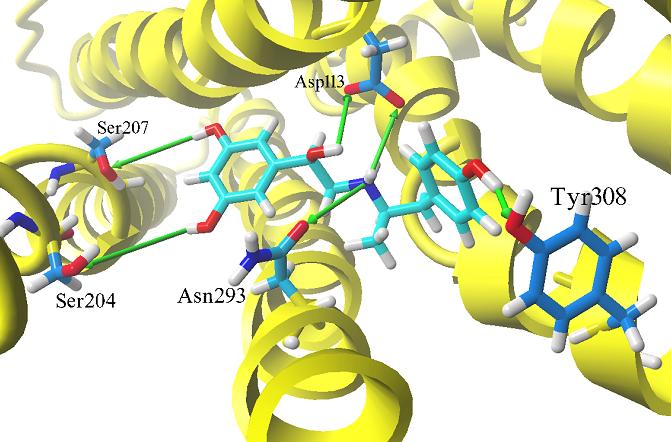
Figure 1. The binding site of β2-AR and the 3D model of (R,R)-fenoterol-β2-AR complex. |