| Search for content and authors |
Two crystalline forms of sarcosine sarcosinium hydrogen L-tartrate |
| Michel Fleck 1, Vahram V. Ghazaryan 2, Aram M. Petrosyan 2 |
|
1. Institute of Mineralogy and Crystallography, Althanstraße 14, Wien 1090, Austria |
| Abstract | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
In continuation of our work on salts of amino acids with dimeric cations [1] we have investigated some new crystalline salts of sarcosine with sarcosine sarcosinium dimeric cation: (Sar···Sar+)Cl–, (Sar···Sar+)Br–[2], (Sar···Sar+)I– [3], (Sar···Sar+)BF4–, (Sar···Sar+)ClO4– [4], (Sar···Sar+)NO3– [5]. With this contribution, we present our results on the system sarcosine + L-tartaric acid + H2O. In particular, we wanted to find out if salts with dimeric cation of the type Sar···Sar+ (as have been established in other sarcosine salts [2-5]) could be found in this system. In addition to the previously reported crystal sarcosinium hydrogen L-tartrate (I) [6], we have identified two new phases (II) and (III), which turned out to be polymorphs of sarcosine sarcosinium hydrogen L-tartrate (Table 1). Both phases were investigated by means of single crystal XRD and vibrational spectroscopy, and found to contain a zwitter-ionic sarcosine, a sarcosinium cation, and a hydrogen L-tartrate anion in the asymmetric unit, i.e., they represent a 2:1 ratio of constituents. It is worth noticing that both species crystallize in the same symmetry, viz. the orthorhombic space group P212121, but have a different arrangement of building units. The expected dimeric Sar···Sar+ cation was found in phase (III) only, whereas in (II) the sarcosinium cation forms a strong O–H···O hydrogen with the carboxylate group of the hydrogen L-tartrate anion bond (O···O distance of 2.4553(15) Å). The carboxyl group of the anion forms in turn an O–H···O bond towards the carboxylate group of the third molecule in the asymmetric unit, viz. the sarcosine zwitter-ion (O···O distance of 2.5065(14) Å, Fig. 1). In contrast, the building unit in (III) are said dimeric sarcosine sarcosinium cations (O···O distance of to 2.512(3) Å) as well as the hydrogen L-tartrate anions, forming hydrogen bonded infinite 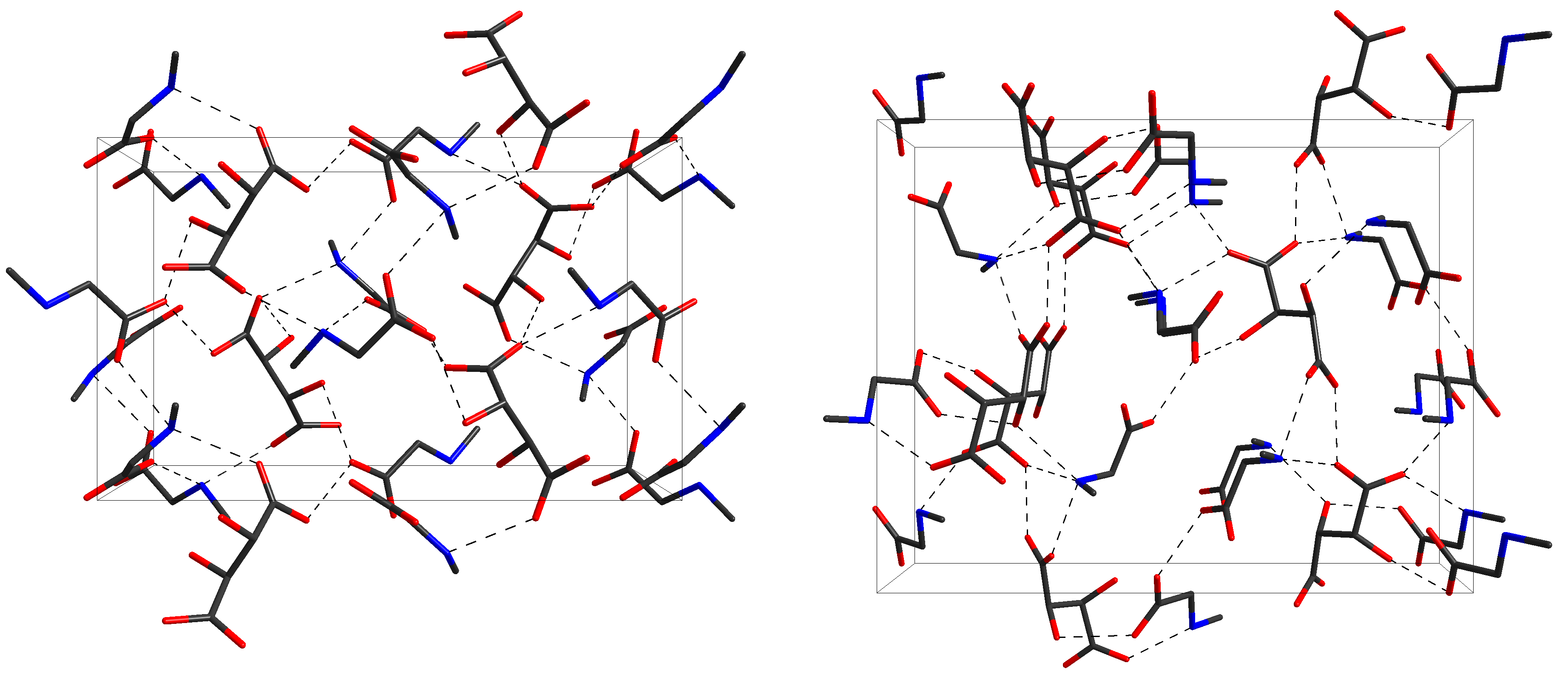
Fig. 1. Crystal structures of forms (II, left) and (III, right) of sarcosine sarcosinium hydrogen L-tartrate. Note the differences in arrangement and conformation. chains (O···O distances between carboxyl and carboxylate groups of to 2.510(2) Å). In addition, one more phase (IV) was identified by its infrared spectrum without structure determination. Concluding, we found that the system sarcosine + L-tartaric acid + H2O contains at least four phases, three of which have been characterized structurally. In addition to the previously known species (I) Sar+·L-tartrate–, two 2:1 compounds were found, which have the same symmetry but different arrangements of constituents, i.e., Sar+···L-tartrate–···Sar (II) and (Sar···Sar+)·L-tartrate– (III). This pair of crystals represents an example of dimorphism where both structures have the same space group and comparable unit cell size (as can be seen by the value of Z). Such examples are rare, but have been found before (e.g. [7, 8]).
Table 1. Crystal data for two forms (II and III) of sarcosine sarcosinium hydrogen L-tartrate, compared with sarcosinium hydrogen L-tartrate (I) [6]. All sets measured at ambient conditions.
References [1] V. V. Ghazaryan, M. Fleck, A. M. Petrosyan, New salts of amino acids with dimeric cations. Proc. SPIE 7998 (2011) 79980F. [2] V.V. Ghazaryan, M. Fleck, A.M. Petrosyan, Sarcosine sarcosinium chloride and sarcosine sarcosinium bromide, J. Mol. Struct. 1020, 160-166(2012). [3] V.V. Ghazaryan, M. Fleck, A.M. Petrosyan, Iodides of sarcosine. J. Mol. Struct. 1032, 35-40(2013). [4] V.V. Ghazaryan, M. Fleck, A.M. Petrosyan, Sarcosine sarcosinium tetrafluoroborate and sarcosine sarcosinium perchlorate: synthesis, structure and vibrational spectra, J. Mol. Struct. 1021, 130-137(2012). [5] M. Fleck, V.V. Ghazaryan, A.M. Petrosyan, Crystal structure at 296 and 150K, vibrational spectra and thermal behaviour of sarcosine sarcosinium nitrate. Z. Kristallographie 227(12), 819-824(2012). [6] R.V. Krishnakumar, M. Subha Nandhini, S. Natarajan, Sarcosinium tartrate. Acta Crystallogr. C57 (2001) 165-166. [7] N. Nagel, H. Bock, P. Eller, Dimorphism and inclusion compounds of N,N'-di(benzenesulfonyl)-p-phenylenediamine. Acta Crystallogr. B56 (2000) 234-244. [8] J.P. Jasinski, R.J. Butcher, K. Veena, B. Narayana, H.S. Yathirajan, A second polymorph of (2E)-1-(4-fluorophenyl)-3-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)prop-2-en-1-one. Acta Crystallogr. E65 (2009) o1965-o1966. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Auxiliary resources (full texts, presentations, posters, etc.) |
|
| Legal notice |
|
| Related papers |
Presentation: Poster at 17th International Conference on Crystal Growth and Epitaxy - ICCGE-17, Topical Session 7, by Aram M. PetrosyanSee On-line Journal of 17th International Conference on Crystal Growth and Epitaxy - ICCGE-17 Submitted: 2013-03-21 14:40 Revised: 2013-03-22 08:50 |