Nowadays, there is the growing interest in new active heterocyclic stuctures with different biologically and pharmacologically activity. Our synthetic research focuses on preparation of new series of active compounds and their structure and potential pharmacological properties elucidations. The main objectives are as follows:
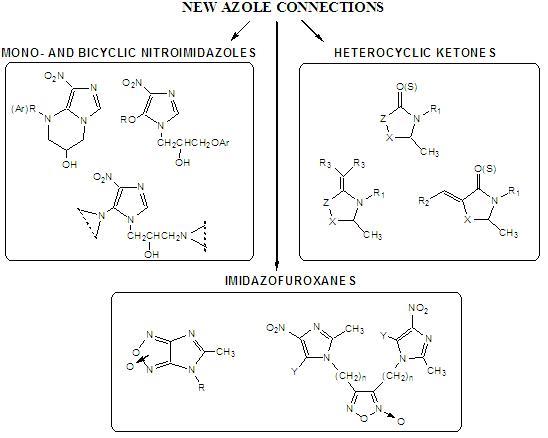
- bicyclic and monocyclic derivatives of nitroimidazoles as potential tuberculostatic agents - it was taking the atempt of the nucleophilic substitution of chlorine atom in 2-chloromethylnitroimidazodihydrooxazoles with different nucleophiles e.g. secondary cyclic amines. Unstability of dihydrooxazole ring was observed and it was used for bulding of new, six-membered tetrahydropyrimidyne ring, condensed with nitroimidazole by the reaction with compounds having primary amino-group,
- heterocyclic ketones as a kind of natural jasmone analogues - based on pyrrolidinone, oxazolidinone, thiazolidinone systems - as fragrant compounds that have the ability to stimulate the same receptors as jasmone and exhibit intresting and persistent fragrant properties. It has been decided to subject its to further chemical modifications, for example with the use of reactive carbonyl group for the nucleophilic substitution reactions resulting in appropriate thionated or malonilydene derivatives. Presence of carbonyl group also affect the increase in acidity of the hydrogen atoms linked to carbons atoms in alfa position and it creates favorable conditions for numerous reaction of condensations e.g. with selected aldehydes leading to new fragrant adducts,
- active imidazole derivatives containing furoxan moiety and evaluation of their ability to relase nitric oxide with use medicinal chemical hybridization, which involves the combination of two complementary biological activities by joining appropriate groups directly or via linker. Broad biological significance of furoxanes and their fused derivatives led to attempt a synthesis of such systems. The furoxan ring is formed by the oxidative cyclization of appropriate alfa-dioximes. It is planed to obtained series furoxan systems conjugated directly or through alkyl chain with two imidazolyl moieties. Preliminary experiences have showed that fused furoxanes which will combine elements of the known biologically active structures e.g. imidazoles were obtained in oxidative cyclization of respective o-aminonitro compounds under the influence of sodium hypochlorite. In situ test imidazofuroxanes obtained showed different biological activity, mainly as vasodilator, antianginal and antiischemic agents.
Most of the above mentioned compounds were tested in many biological activity directions.
|